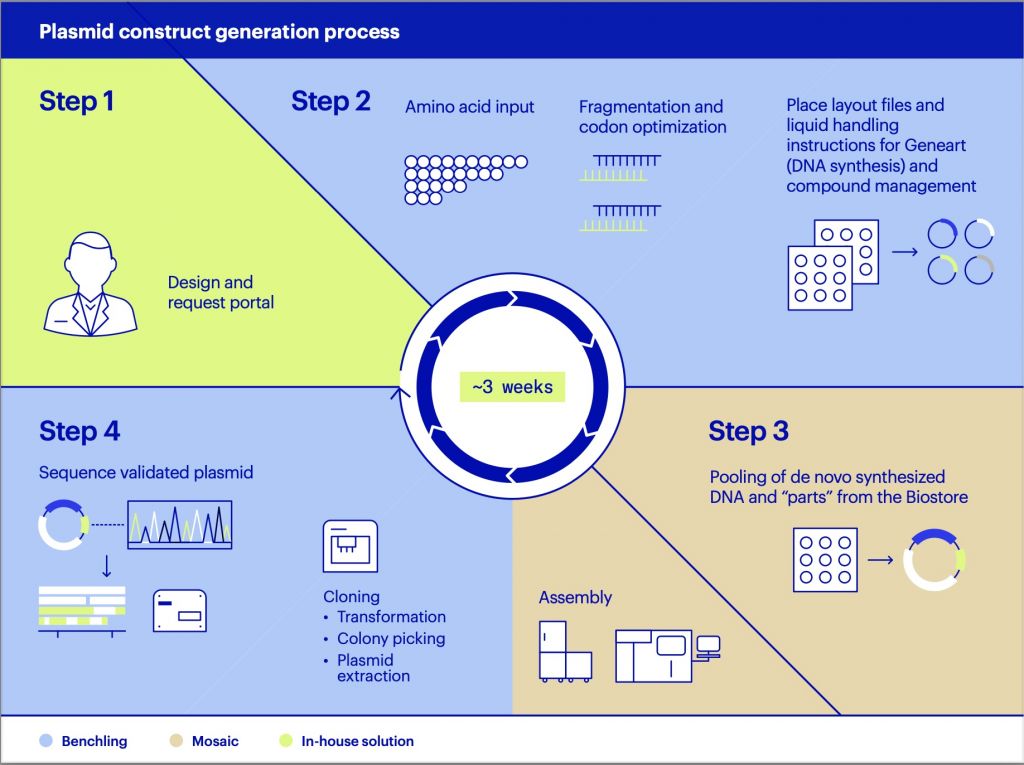
These days, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are everywhere. From self-driving cars to facial recognition to photograph-refinement software—AI and ML are being applied to a variety of fields in myriad ways.
AI and ML are also becoming omnipresent throughout NHGRI and in genomics. Within the NHGRI Intramural Research Program, several researchers have been using AI to characterize genomic disorders and learn how to communicate genomic risk. For example, Benjamin Solomon, M.D., and his colleagues are using these computational tools to recognize and classify rare genetic skin conditions. Oleg Shchelochkov, M.D., recently led a study using ML to find biomarkers associated with mild and severe forms of propionic acidemia, a genetic condition that affects digestion of proteins and fats. Currently, Susan Persky, Ph.D., is using AI tools to understand how different ways of communicating genomic information can influence peoples’ behavior. These experiences reveal the wide applicability of AI and ML in different areas of contemporary genomics research, including considerations of many ethical, legal, and social implications.
The use of AI and ML is also increasing across the NHGRI portfolio of extramural grants, which fund both basic and clinical genomics research. For example, NHGRI currently supports extramural research that aims to improve the accuracy of DNA sequencing by using AI and ML to identify the correct DNA base using the raw signals generated by the sequencing process. With other grants, researchers are using AI to predict the functional influences of genomic variants, with a focus on gene expression. Lastly, ML is being used for improving the methods for calculating polygenic risk scores, which reflect an individual’s genetic risk for a trait or disease.
ML represents a subcomponent of AI, and beyond its use in genomics research, ML is helping historians probe the history of genomics. Spencer Hong, a graduate student in Luís Nunes Amaral’s research group at Northwestern University, uses ML to categorize and analyze materials in NHGRI’s historical document archive, which contains over two million pages of emails, letters, reports, and other documents pertaining to the history of genomics and NHGRI. ML tools analyze and characterize these diverse documents much faster than humans can manually, making ML valuable for studying the history of genomics and NHGRI’s role in shaping the field.
NHGRI has hosted events to engage researchers and the public about the roles of AI and ML in genomics. For example, in December 2022, NHGRI held a Twitter Q&A with Hong, who answered questions about his research. In 2021, the institute convened a workshop entitled “Machine Learning in Genomics: Tools, Resources, Clinical Applications, and Ethics Workshop” that identified key areas in genomics ripe for ML applications. That event also helped to define NHGRI’s unique role in ML research in both basic genomic science and genomic medicine.
At the NIH level, the Common Fund recently launched the Bridge to Artificial Intelligence (Bridge2AI) Program, which aims to propel biomedical research forward by setting the stage for widespread adoption of AI to tackle complex biomedical challenges beyond human intuition. The goals of Bridge2AI are to generate flagship AI-ready datasets centered around biomedical grand challenge questions; to emphasize ethical AI best practices for biomedicine; and to establish diverse groups who span the boundary between AI and healthcare research. Bridge2AI includes projects with major genomics components.
Ten years ago, it was hard to imagine that digital voice-assistant devices could readily play music or provide the weather forecast on command without first typing in a request on a computer. In the next few years, it will be fascinating to watch how AI and ML reveal new insights about the human genome and advance the use of genomics in medicine.