New York City detectives questioning a boy facing a felony charge last year offered him a McDonald’s soda. When the boy left, they took the straw and tested it for his DNA.
Although it did not match evidence found at a crime scene, his DNA was entered into the city’s genetic database. To have it removed, the child’s family had to petition a court and file an appeal, a process that took more than a year. The boy was 12.
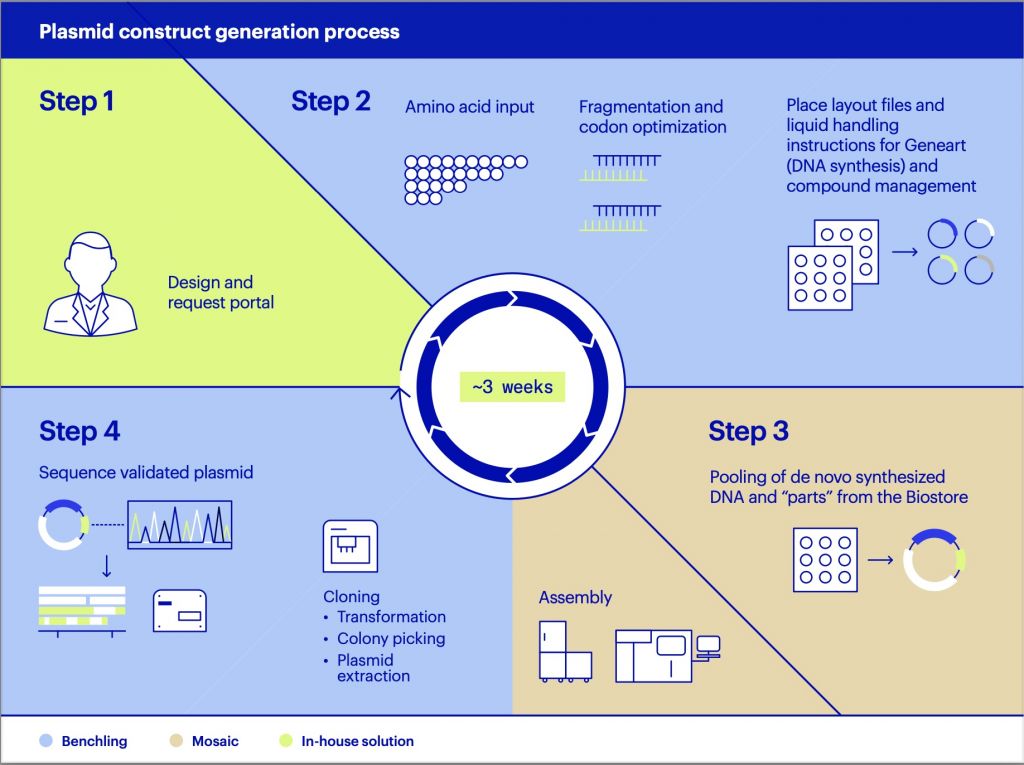
The city’s DNA database has grown by nearly 29 percent over the last two years, and now has 82,473 genetic profiles, becoming a potentially potent tool for law enforcement but one that operates with little if any oversight.
The New York Police Department has taken DNA samples from people convicted of crimes, as well as from people who are only arrested or sometimes simply questioned. The practice has exposed the Police Department to scrutiny over how the genetic material is collected and whether privacy rights are being violated, civil liberties lawyers said.
A growing number of law enforcement agencies throughout the country — including police departments in Connecticut, California and Maryland — have amassed genetic databases that operate by their own rules, outside of state and federal guidelines, which tend to be far more strict.
According to a 2013 survey, 30 states and the federal government permitted the analysis of DNA samples collected from individuals who are arrested or charged, but not convicted, of certain crimes. These databases generally did not include low-level offenders.
New York State law requires a conviction before someone’s DNA can be included in the state-operated DNA databank. But databases built by local authorities are not subject to the state rules.
The rapidly expanding DNA database in New York, which the Office of the Chief Medical Examiner has maintained since it was established in 2009, provides another striking example of the Police Department’s ability to adopt advancing technology with little scrutiny. The department also has built a giant facial recognition database and has been loading thousands of arrest photographs of children and teenagers into it.
The Police Department’s chief of detectives, Dermot F. Shea, said in an interview that officers were engaging in legally permitted law enforcement tactics in building the database.
“We are not indiscriminately collecting DNA,” he said. “If we did, it would be a database of millions and millions.”
Police officials also point out the database has been used to capture scores of violent criminals and to exonerate the wrongly accused. About half of the profiles in the database are from evidence collected from crime scenes. “We use DNA as a truth-finding mechanism,” Deputy Chief Emanuel J. Katranakis said. “It’s unbiased.”
Still, the DNA database, known as the Local DNA Index System, has grown with the addition of DNA from cigarettes, coffee cups, water bottles and other objects touched by people during interviews, even if they are never arrested or the charges are later dismissed.
About 31,400 of the DNA profiles in the city’s database came from people who were arrested or merely questioned in connection with a crime, but may not have been convicted, according to the Legal Aid Society, which obtained details about the database through a Freedom of Information Act request.
One of those was the 12-year-old whose DNA was collected from a straw he used while talking to the police in March 2018. The felony charge against him was eventually dropped, but his DNA remained in the database for more than a year, his lawyer, Christine Bella, said.
The legal ordeal of getting it expunged has left his mother distraught with worry about how her son will view the police going forward. The boy himself has “moved on with his young life,” Ms. Bella said.
Some civil liberties lawyers assert that the methods used to add to the database can violate the Fourth Amendment’s ban on “unreasonable searches and seizures,” a core constitutional principle. They contend the police should not be allowed to take someone’s DNA without probable cause to suspect that they did something illegal.
“It’s essentially saying, ‘Give us your entire genome, even though we don’t have any reason to believe you have committed a crime,’” said Erin E. Murphy, a New York University law professor who has written about DNA databases and DNA profiling.
Terri Rosenblatt, a staff lawyer with the Legal Aid Society, said the practice of taking DNA from water bottles and cigarettes that are offered during interviews, and then loading them into the database, also has undermined public confidence in the police.
“We talk about community policing and the idea that communities should trust their police departments, but all of these kinds of actions erode that trust,” she said.
Defense lawyers have said that the database’s rapid expansion stems, in part, from an aggressive push by the Police Department to collect DNA from every firearm police recover in order to strengthen prosecutions.
The role of the DNA database in investigations became a flash point in the trial of Chanel Lewis, a Brooklyn man convicted in April of murdering Karina Vetrano, a jogger in Queens.
Mr. Lewis’s defense lawyers had argued that DNA evidence collected from the crime scene was tainted and that detectives had conducted “a race-biased dragnet.”

Mr. Lewis was asked to give a DNA sample, based largely on a police lieutenant’s hunch. He was charged with murder after his profile matched DNA found on the victim’s body and cellphone.
But before his arrest, detectives had sought saliva samples from more than 360 black men who had been previously arrested or questioned in parts of Queens and Brooklyn.
‘Race-Biased Dragnet’: DNA From 360 Black Men Was Collected to Solve Vetrano Murder, Defense Lawyers Say

Though the DNA of those men did not match a sample found on Ms. Vetrano’s body, it was still entered into the city’s database and can now be tested, indefinitely, against evidence found at crime scenes throughout the city, defense lawyers said.
The police said that, in most cases, they gained consent before taking DNA samples. But in interviews, several men contacted by the police during the Vetrano investigation said that detectives tried to cajole, bully and threaten them into giving a DNA sample. Some gave in.
Luis Ortiz, a public defender who represented one of the men, said the police arrested his client on a marijuana-related offense and kept him jailed for a day in a Queens precinct until he agreed to a saliva sample. The man, who requested that his name not be published to protect his privacy, said one detective told him, “We know it wasn’t you, but we want to make sure.”
“He felt powerless and like he didn’t have any choice,” Mr. Ortiz said.
Eric Bellamy, 39, said four detectives arrived unannounced at his home in Brooklyn in late 2016 and explained that they wanted a sample of his DNA to eliminate him as a suspect in a murder investigation. Stunned, he refused because the detectives did not have a warrant.
Mr. Bellamy recalled one of the detectives said, “If you’re innocent, what’s the problem?”
Maurice Sylla, 55, said detectives came to his home in Brooklyn in August 2016 seeking his DNA. He was not home, but he said the police asked his niece intimidating questions about the family’s immigration status. The investigators “had no reason to invade my privacy,” he said.
Others questioned during the Vetrano investigation included Amaral Bordenave, 26, who agreed to give a urine sample after the police arrested him on an unrelated gun possession charge, and Justen Henderson, who consented to have his cheek swabbed for DNA after being arrested on a misdemeanor assault charge.
Mr. Henderson said he initially declined to provide the sample, but an officer threatened to lose the paperwork on his case so that he would be in custody longer and might be sent to Rikers Island.
“I didn’t feel like fighting,” Mr. Henderson said. “I wanted to go home.”
Law enforcement officials say the database has turned out to be a powerful tool. The Brooklyn district attorney’s office, for instance, said it had solved more than 270 cases using DNA from the database, including 10 homicides, 36 sexual assaults and 77 weapons offenses.
One example is the case of a 68-year-old woman who was raped and robbed at knife point in her home in 2016. DNA left by the woman’s attacker was uploaded to the city’s database, where it matched Willie Weathers, who had been convicted of a robbery. Mr. Weathers was convicted of the rape and sentenced to 25 years in prison in 2017.
In 2014, the database also helped Brooklyn prosecutors convict another accused rapist, Avery Bovell. Two years after the attack, Mr. Bovell was arrested and questioned in connection with a commercial burglary. The police obtained a sample of his DNA from an object he touched, and it matched the DNA of one of two men the victim said had raped her. In June, Mr. Bovell pleaded guilty to first-degree criminal sexual act.
“Without having that resource, we would never have been able to identify one of the attackers in that case,” said Rachel Singer, the chief of the forensic science unit in the Brooklyn district attorney’s office.
Once a person’s genetic information has been put in the database, it can be a struggle to get it removed, lawyers said. Last year, the medical examiner’s office removed only seven DNA profiles from the database.
Take, for example, the case a Bronx man, Lamar, who asked that his last name be withheld to protect his privacy. In April 2018, detectives questioned him about a firearm they believed he had discarded and surreptitiously collected his DNA from a cigarette they had offered him, video of the interrogation shows.
When the charges against him were later dismissed, Lamar petitioned a judge to expunge his DNA from city records. He said he did not learn that detectives had collected his DNA from the cigarette until it was revealed at a court hearing. “I didn’t expect nothing like that,” he said.
Genealogy Sites Have Helped Identify Suspects. Now They’ve Helped Convict One.
She Was Arrested at 14. Then Her Photo Went to a Facial Recognition Database.
Police Agencies Are Assembling Records of DNA